Carbohydrates give the body energy to go about your day's mental and physical tasks Digesting or metabolizing carbohydrates breaks foods down into sugars, which are also called saccharides TheseDigestion of Carbohydrates During digestion, starches and sugars are broken down both mechanically (eg through chewing) and chemically (eg by enzymes) into the single units glucose, fructose, and/or galactose, which are absorbed into the blood stream and transported for use as energy throughout the bodyCorn chips are a snack food made from whole corn, corn oil and salt Because corn chips are made out of the starchy vegetable corn, they are rich in carbohydrate Carbohydrate is a type of nutrient that, unlike protein and fat, turns into sugar Carbohydratecontaining foods – including corn chips – break down into glucose sugar molecules during your body's digestion process
Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute
Carbohydrates break down into sugar (glucose) during digestion
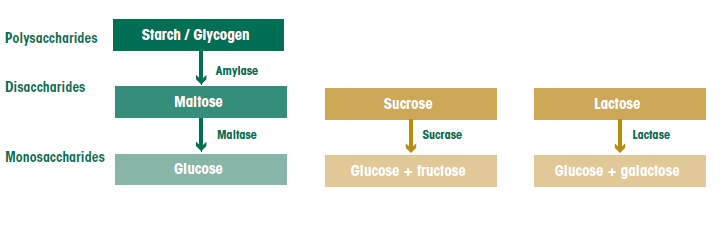
Carbohydrates break down into sugar (glucose) during digestion-Complex carbohydrate are made of multiple sugar molecules strung together like a necklace or branched like a coil they are slower digesting and rich in fiber glycogen the complex carbohydrate molecule used to store carbohydrates in the liver and muscle cells when carbohydrate energy is needed, glycogen is converted into glucose for use The goal of carbohydrate digestion is to break down all disaccharides and complex carbohydrates into monosaccharides for absorption, although not all are completely absorbed in the small intestine (eg, fiber) Both simple and complex carbohydrates break down into glucose (aka blood sugar) A simple carb is one that's comprised of one or



Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute
Our bodies change 100 percent of the carbohydrate we eat into glucose This affects our blood sugar levels quickly, within an hour or two after eating Protein Includes fish, meat, cheese, and peanut butter The glucose from fat is absorbed slowly and it won't cause an immediate rise in blood sugar Glucose metabolism by Pancreas Glucoregulation – Insulin and Glucose level in the body Glucoregulation is the regulation of steady levels of glucose in the blood & body The hormone "Insulin" plays a vital role in the utilization of glucose by the body cells Glucose cannot enter the muscle cells, once there is no insulin in the blood stream Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars that are used by the body for energy As carbohydrates are eaten, the digestive tract breaks them down into monosaccharide units, or glucose The glucose enters the bloodstream and travels first to the brain, which runs entirely on energy from glucose After the glucose needs of the brain have
The goal of digestion and absorption of carbohydrates is to break them down into small molecules of sugar known as glucose Glucose is a primary fuel that drives the metabolism and function ofFructose is the primary sugar in fruit Other common disaccharides are maltose (malt sugar) and lactose (milk sugar) Chemical terms ending inose indicate sugar The Digestion Process At the cellular level, your body uses glucose and oxygen to perform its many amazing functions All sugars and other carbs need to be broken down into easilyused monosaccharides After you swallow, sugar and other foods travel down the esophagus via peristalsis into the stomach and then the small intestines Here, sugars
The three types of carbohydrates are sugar, starch and fiber During the digestive process, both sugars and starches are turned into the sugars that the body uses forCarbohydrate Digestion & Fermentation These enzymes, in the mouth and the small intestine, are able to break down many sources of carbohydrate into simple sugars and oligosaccharides, but are incapable of digesting many more animal and especially plant polysaccharides the gut microbiota absorb glucose and other sugars after degrading The digestive tract begins to break down carbohydrates into glucose, which is used for energy, upon consumption Any extra glucose in the bloodstream is stored in the liver and muscle tissue until further energy is needed Carbohydrates is an umbrella term that encompasses sugar, fruits, vegetables, fibers, and legumes



Small Intestine Digestion Absorption Teachmephysiology



Discover The Good And Bad Of Carbohydrate
The body breaks downor converts most carbohydrates intothe sugar glucose Glucose is absorbed intothe bloodstream, and with the help of a hormone called insulin it travels intothe cells of the body where it can be used for energy Which is a difference between proteins and carbohydrates and fats? Digestion The goal of carbohydrate digestion is to break down all disaccharides and complex carbohydrates into monosaccharides for absorption, although not all are completely absorbed in the small intestine (eg, fiber) Digestion begins in the mouth with salivary amylase released during the process of chewing Carbohydrates Submitted by Thiruvelan on Wed, The complex carbohydrates are broken down in the digestive tract to simpler sugar (or glucose) This sugar is primarily useful for the production of energy by oxidation What is Carbohydrate?




Carbohydrates In Pet Food Pfma



15 3 Digestive System Processes Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
And sucrose, more commonly known as refined white sugarSimple carbs are classified as being "simple" because they EASILY break down in one simple step in your gut For example when you eat an apple, simple carbohydrate fructose molecules head directly to your small intestine Glucose Complex carbs get broken down into glucose;Carbohydrates 1 Carbohydrates are broken down into monosaccharides by enzymes called maltases, isomaltases, and "4 When the body needs energy, the glycogen is broken down into glucose and used by the cells for energy 5 Fiber is a "4 Glucose is also transported to the muscles and other




Carbohydrates Sciencedirect




Learn About Carbohydrate Digestion Chegg Com
C Specific enzymes break down carbohydrates into simple sugar such as glucose D Specific hormones break down carbohydrates into fatty acids and glycerol The digestion of food is the break down of complex food substances by the enzymes secreted by various parts of the digestive systemAll of this gives the small intestine a huge surface area for absorption) Figure 413 Digestion and absorption of carbohydrates in the small intestine Fructose and galactose are converted to glucose in the liver Once absorbed carbohydrates pass through the liver, glucose is the main form of carbohydrate circulating in the bloodstreamDuring digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple, soluble sugars that can be transported across the intestinal wall into the circulatory system to be transported throughout the body Carbohydrate metabolism begins in the mouth, where the enzyme salivary amylase begins to break down complex sugars into monosaccharides These can




What Are Carbs And What Do They Do To Us Dr Robert Kiltz
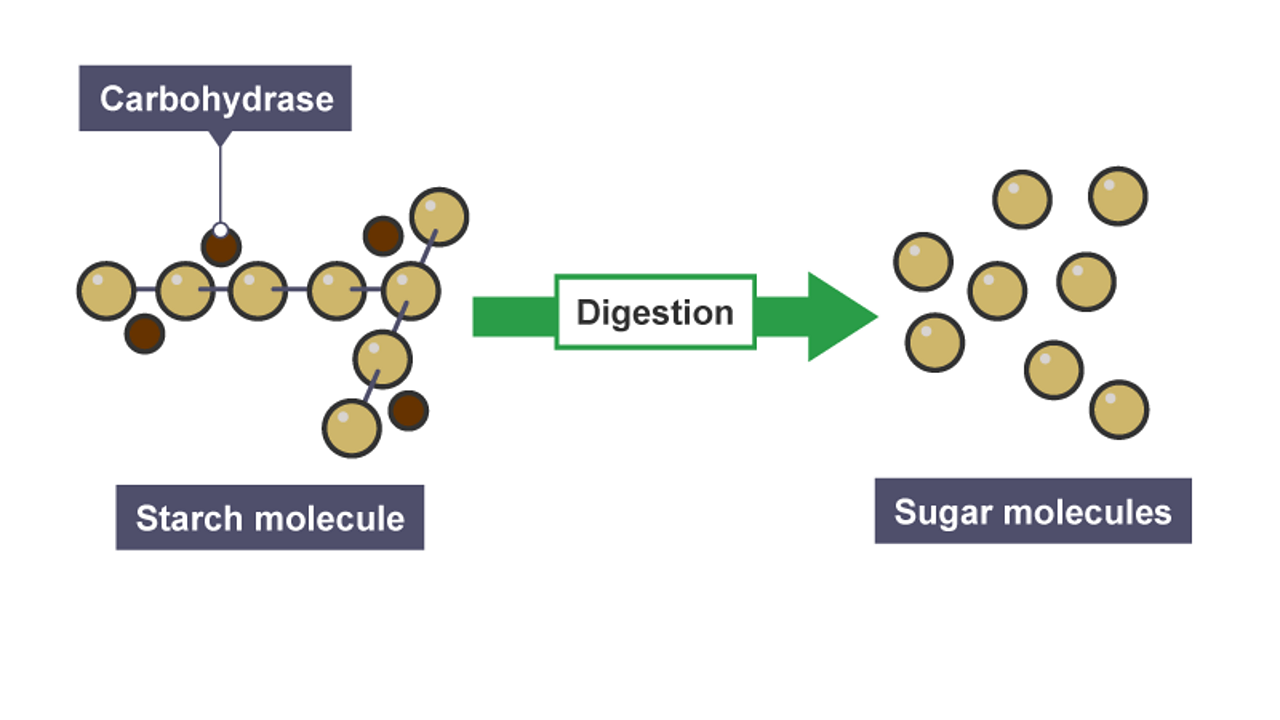



Digestive Enzymes And Absorption Nutrition Digestion And Excretion Ks3 Biology c Bitesize c Bitesize
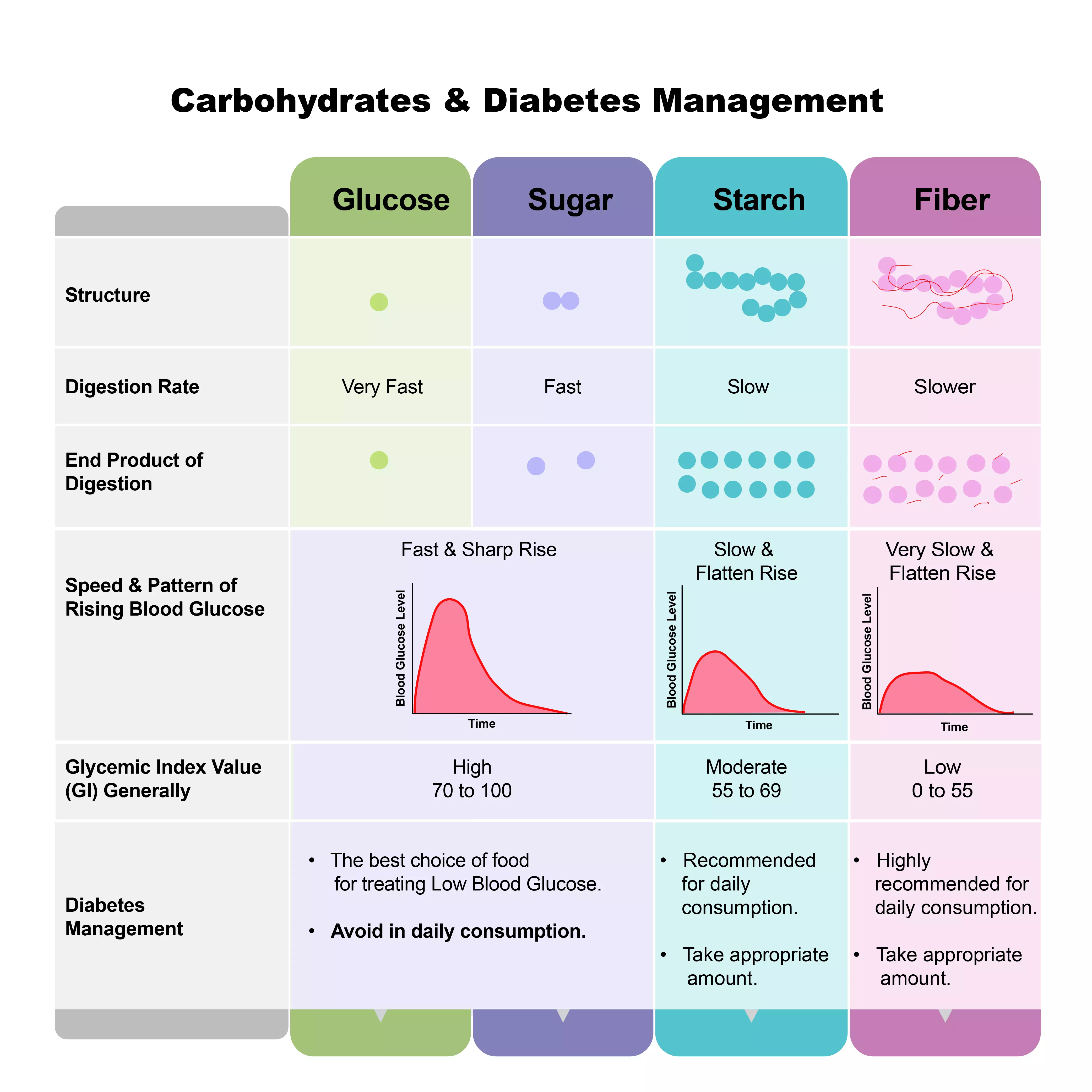
These nutrients are digested into simpler compounds The Glycemic Index (GI) is a measurement that ranks the effects of carbohydrates on our blood sugar levels on a scale of 0 to 100 Carbohydrates that break down quickly during digestion and release glucose rapidly into the bloodstream have a high GI Carbohydrates that break down more slowly and release glucose more gradually into the bloodstream have a low GICarbohydrate is an organic compound that contains carbon, hydrogen, and the oxygen atoms
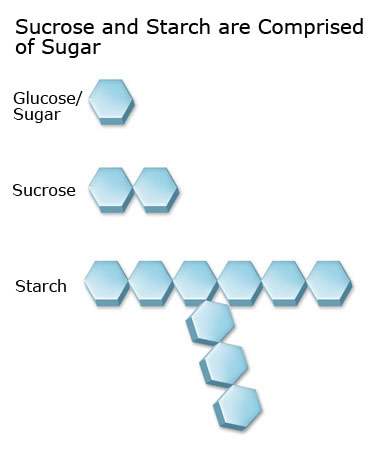



Understanding Carbohydrates Diabetes Education Online




Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute
blood sugar (glucose) level During digestion carbohydrates break down into simple sugars Carbohydrates are absorbed into the bloodstream as blood sugar (glucose) Drinks with sugar (juice, regular soda) Fruit (fresh, canned, dried) Potatoes, corn, peas, beans Complex carbohydrates are starches and broken down more slowly than simple carbs and will raise sugar levels more slowly Note that eating highly refined starches such as white bread will usually result in a sharp rise in blood sugar levels Whole grain foods, which have a greater level of fibre, are a much better choice of starches as the During digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars The most important one is glucose sucrose fructose table sugar 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement VintageRose VintageRose Glucose is one of the most important sugars in your body It is used for a wide variety of tasks including the production of ATP, which powers our




Chapter Chemical Digestion And Absorption Bio 140 Human Biology I Textbook Libguides At Hostos Community College Library
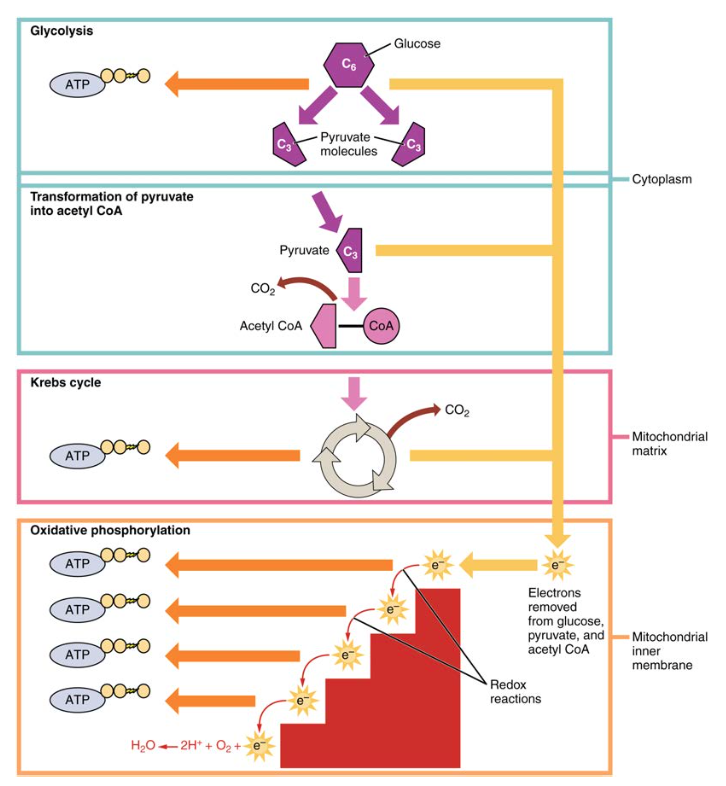



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
How are carbohydrates broken down? Dietary carbohydrates include starches, sugars, and fibre Use of Dietary Carbohydrates as Energy Glucose is the primary energy source of the body Major dietary sources of glucose include starches and sugars Digestion of Carbohydrates Dietary carbohydrates are digested to glucose, fructose and/or galactose, and absorbed into the blood Carbohydrates in food and drinks break down into glucose in the body When people without diabetes eat carbs, their blood sugar rises, and the insulin response kicks in to move the blood sugar to the cells for fuel But in people with type 2 diabetes, the insulin response doesn't work properly, and your blood glucose levels remain elevated




Starch Digestion Bioninja
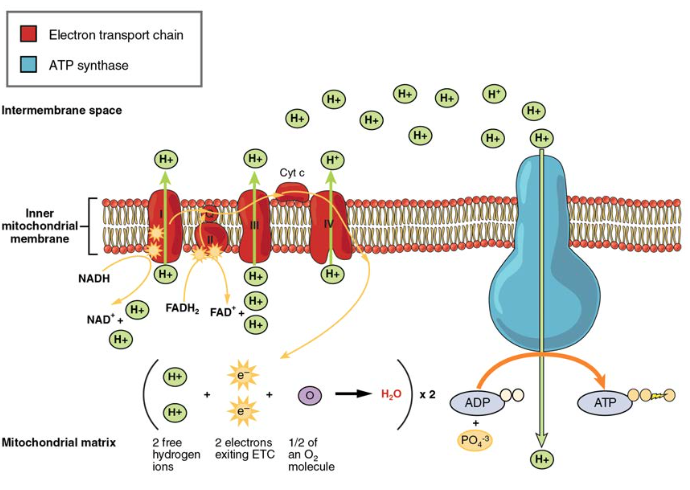



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Lipids (fats and oils) Lipase enzymes break down fat into fatty acids and glycerol Digestion of fat in the small intestine is helped by bile, made in the liver The protein will be converted to blood glucose more slowly than carbohydrates and will keep blood glucose levels from dropping too low during the night The body breaks down or Simple carbs include fructose, or fruit sugar; When we consume disaccharides our bodies break them down into single sugars These sugars are glucose, fructose and galactose, and they are used as energy for our body Lactose, for example, can be found in breast milk and is used as an energy source by infants Likewise, maltose is a sweetener that's regularly used in confectionery like



Types Of Carbohydrates




Carbohydrate And Sugars Terminology The Canadian Sugar Institute
I Visage/Stockbyte/Getty Images Carbohydrate digestion happens in your digestive tract You start to break down some carbs in your mouth, but since your stomach pays more attention to proteins and fats, most carbohydrate digestion takes place in your small intestine Once the carbs are digested into single sugar units, your body absorbs themSucrase breaks sucrose into glucose and fructose molecules Maltase breaks the bond between the two glucose units of maltose, and lactase breaks the bond between galactose and glucose Once carbohydrates are chemically broken down into single sugar units they are then transported into the inside of intestinal cells Both simple and complex carbohydrates break down into glucose (aka blood sugar) A simple carb is one that's comprised of one or two sugar molecules, while a complex carb contains three or more sugar molecules Fiber, on the other hand, is found in healthy carbs, but isn't digested or broken down Explanation Advertisement Answer 0 Brainly User




3 3 Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts
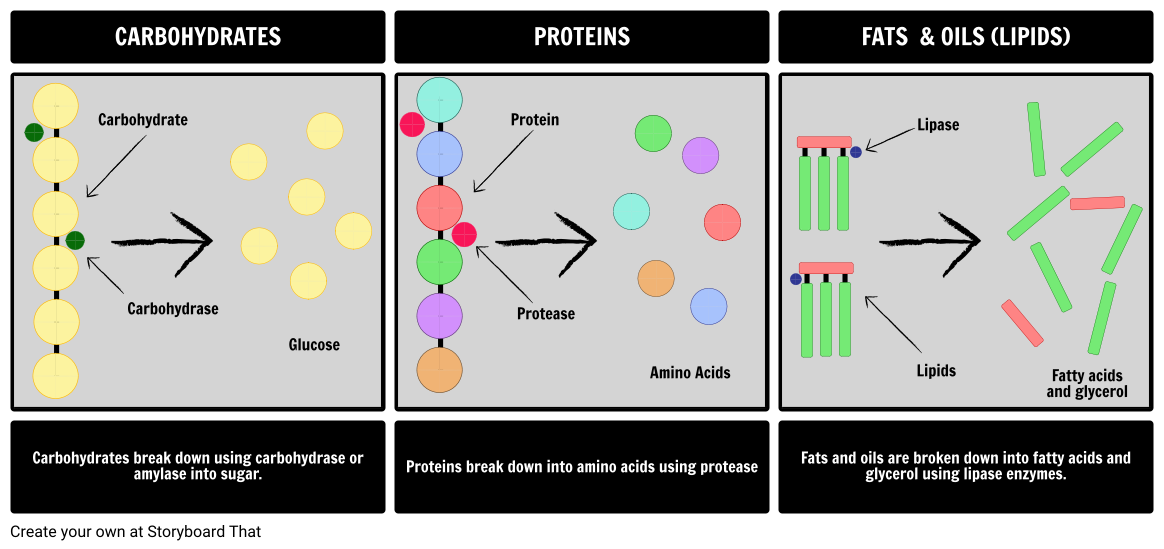



Digestion Carbohydrates Proteins And Lipids Storyboard
During digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars The most important one is glucose Unused glucose that is converted to is stored in the liver glycogen Carbohydrates are found in foods that contain starches and sugar To understand how or why carbohydrates turn into sugar, you need to understand how the digestion process works Carbohydrates come in three major packages sugars, starches and fibersFiber isn't digestible (which means it stays mostly in its full form and doesn't get converted into sugar), so forget about that for a minute and focus on the other two Carbohydrates are digested in the mouth, stomach and small intestine Carbohydrase enzymes break down starch into sugars The saliva in your mouth contains amylase, which is another starch digesting enzyme If you chew a piece of bread for long enough, the starch it contains is digested to sugar, and it begins to taste sweet
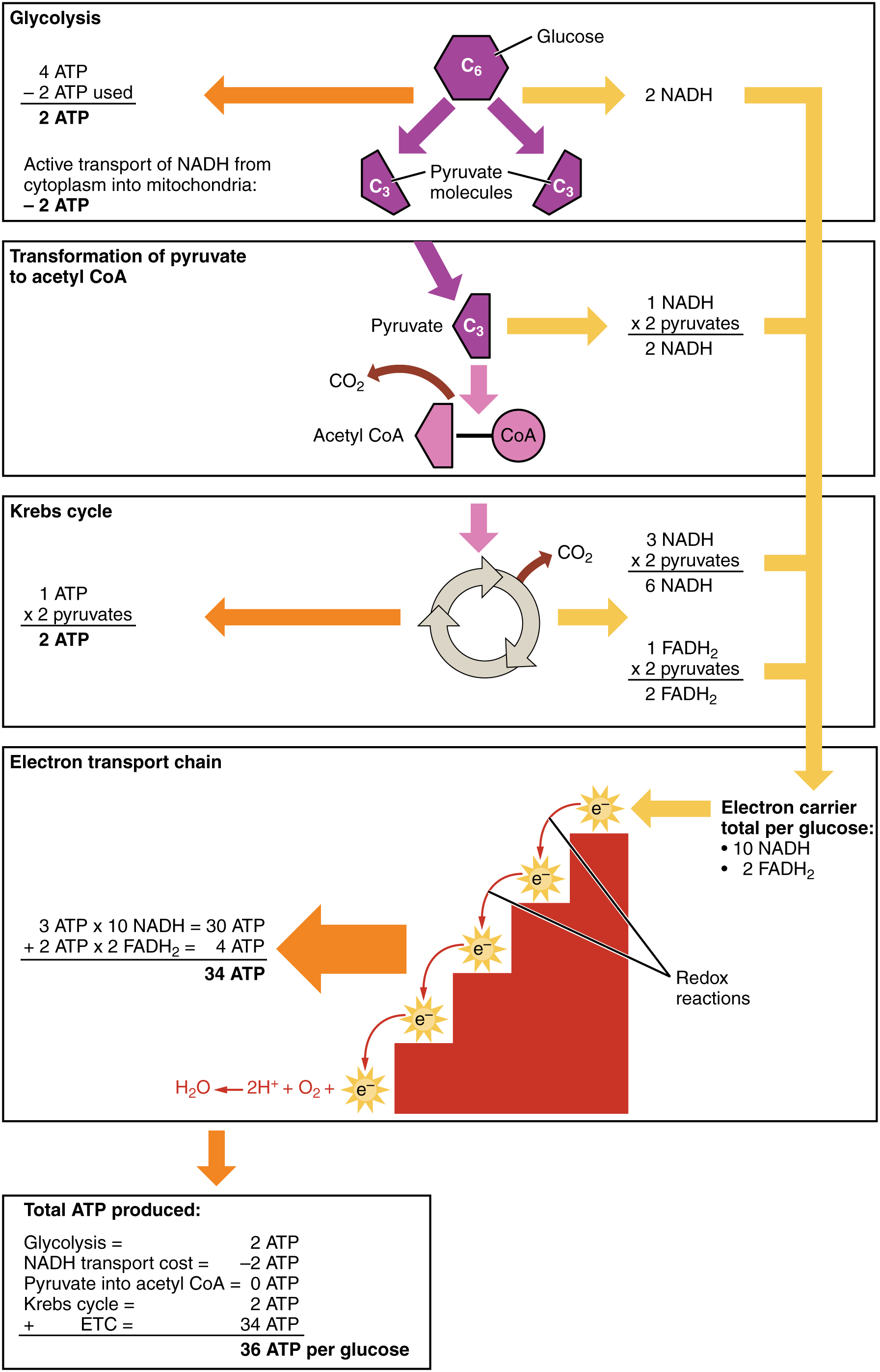



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology



What Do Carbohydrates Do
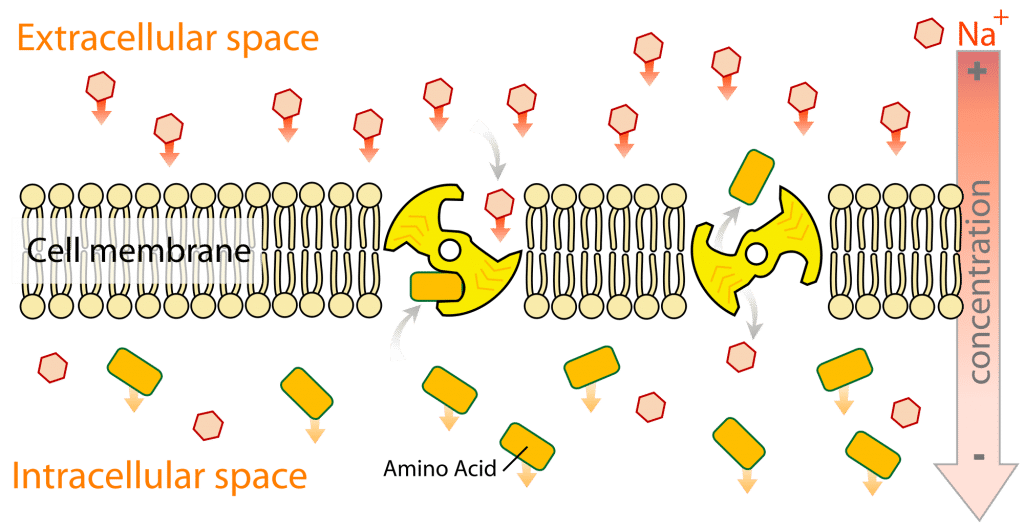
During digestion, a series of enzymatic reactions break down the carbohydrates in these foods into simple carbohydrates that are easily absorbed in the small intestine While complex carbohydrates require enzymes such as salivary amylase, pancreatic amylase and maltose for digestion, simple carbohydrates require little or no enzymatic reactionGlucose – this is one of the most important forms of sugar used by the body for energy All other carbohydrates (including other sugars) are converted into glucose during the digestion of food Glucose is naturally found in some fruits and vegetables and the nectar or sap of plantsFor this reason, digestive enzymes break down carbohydrates into three monosaccharides, namely glucose, galactose, and fructose Monosaccharides are transported to the liver, which turns galactose and fructose into glucose The liver then sends the produced glucose into the bloodstream, where it is transported to the cells that need energy
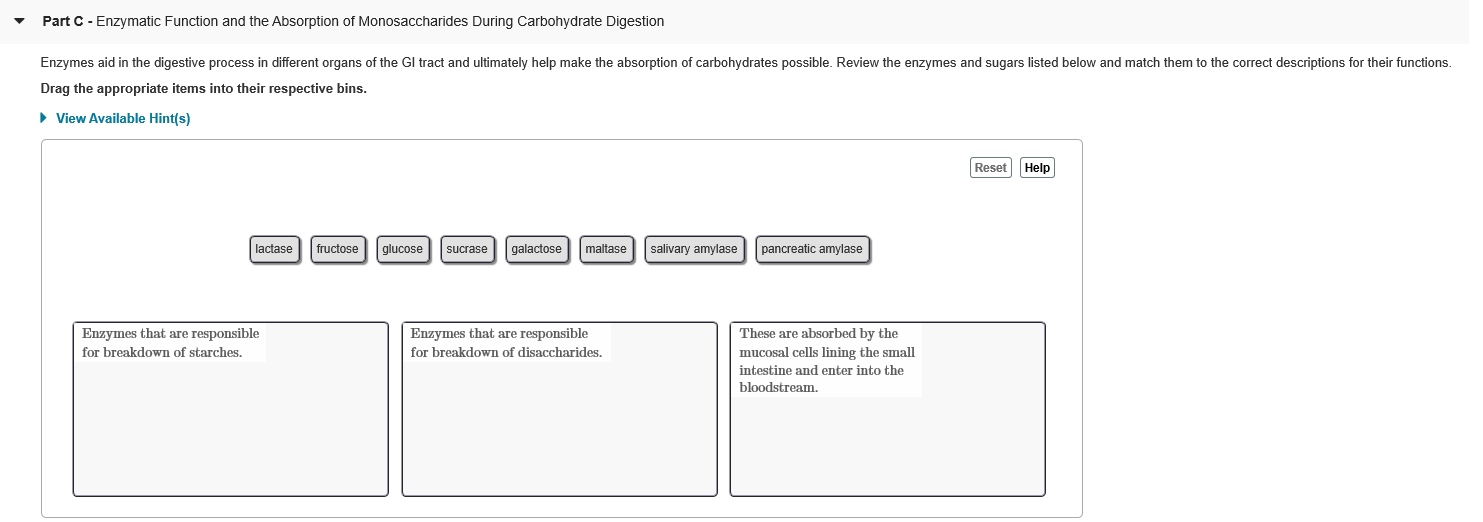



Solved Focus Figure 4 8 Carbohydrate Digestion Overview 4 Chegg Com



2
Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage As cells absorb blood sugar, levels in the bloodstream begin to fallHowever, it requires more process than the breakdown of simple sugar like fructose When you eat foods like toast or mashed potato, the saliva starts acting on it in the mouth The starch is broken down into maltoseSucrose, or common table sugar, is a disaccharide which breaks down during digestion into the simple sugars glucose and fructose Glucose is the primary sugar in blood;
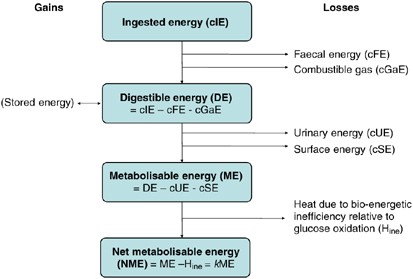



Physiological Aspects Of Energy Metabolism And Gastrointestinal Effects Of Carbohydrates European Journal Of Clinical Nutrition




What Types Of Carbohydrates Turn To Sugar
During digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple, soluble sugars that can be transported across the intestinal wall into the circulatory system to be transported throughout the body Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the It is necessary for this breakdown to occur so the sugar units are small enough to be absorbed out of your digestive tract and into your bloodstream Carbohydrates are disassembled, or broken downLactose, which is milk sugar;




25 3 Digestive System Processes Texas Gateway




Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute
Digestion The goal of carbohydrate digestion is to break down all disaccharides and complex carbohydrates into monosaccharides for absorption, although not all are completely absorbed in the small intestine (eg, fiber) Digestion begins in the mouth with salivary amylase released during the process of chewing




Digestive System Processes Biology For Majors Ii




Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption Carbohydrate Metabolism Youtube



2




Carbohydrates Crossword Wordmint



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Human Nutrition Deprecated



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Human Nutrition Deprecated




Solved Reset Help Autoimmune Disease 1 When Digestible Chegg Com




25 3 Digestive System Processes Texas Gateway
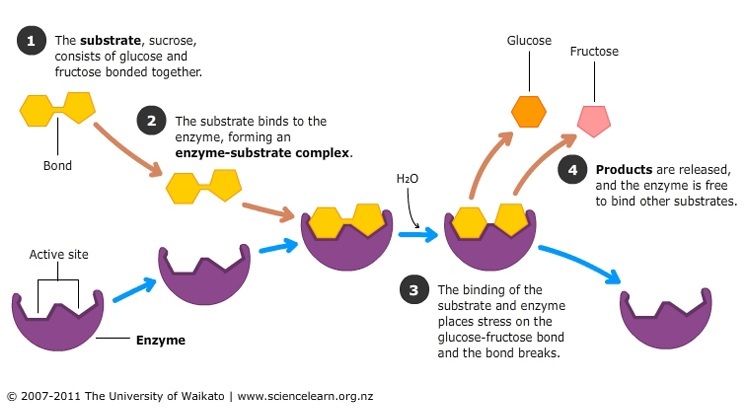



Digestion Breaking The Large Into The Small Science Learning Hub
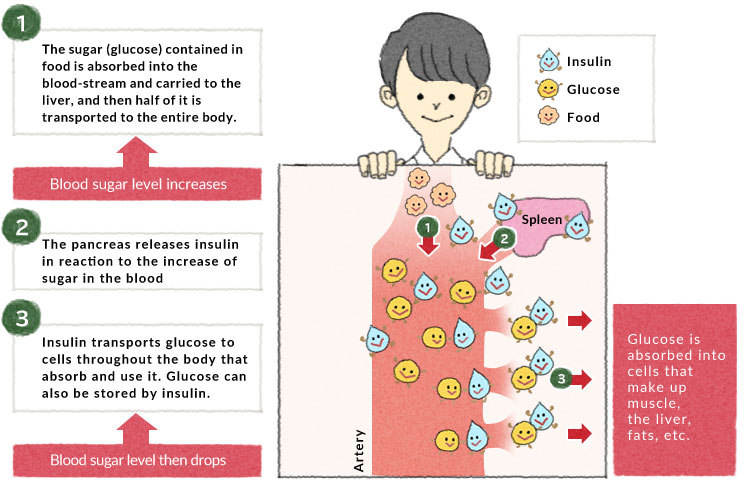



The Relationship Between Blood Sugar Level And Gi Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co Ltd
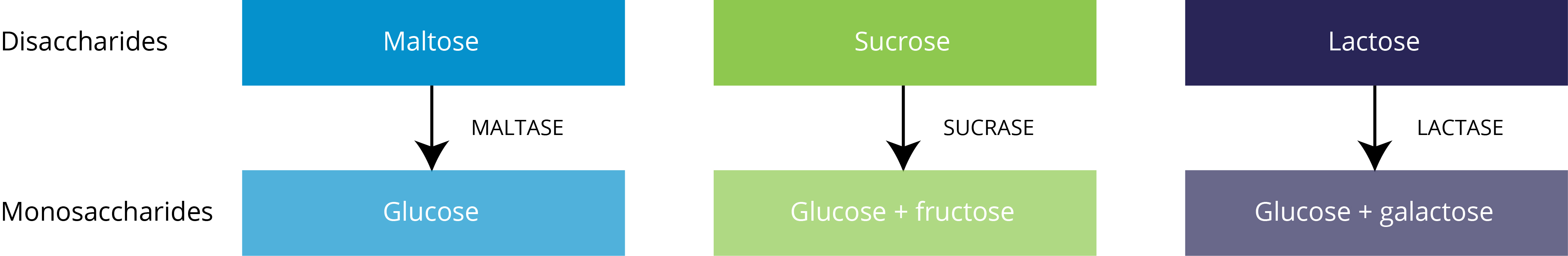



What Happens To Disaccharides During Digestion Sugar Nutrition Resource Centre
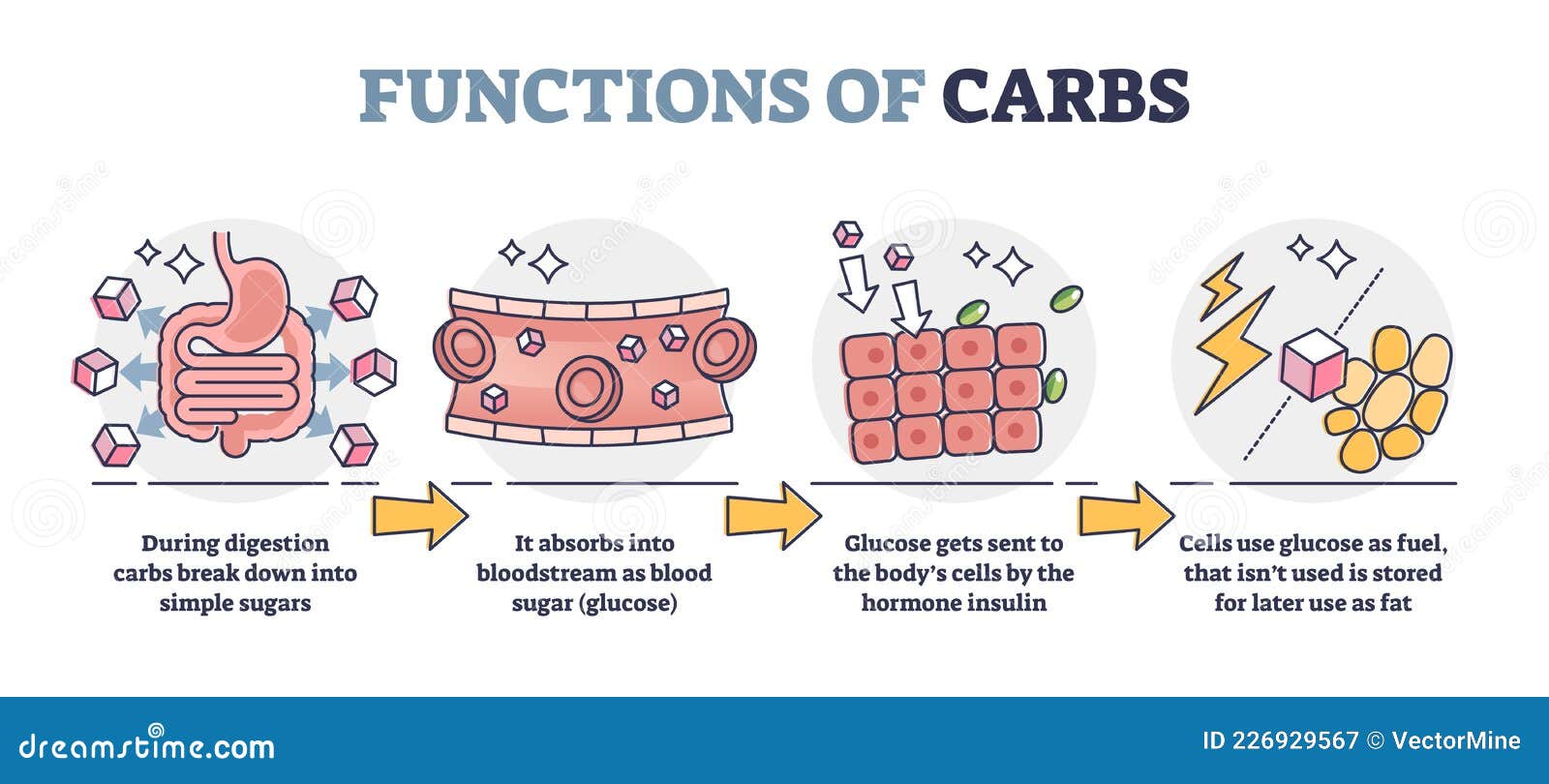



Functions Of Carbs And Carbohydrates In Digestive System Outline Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Protein Concept
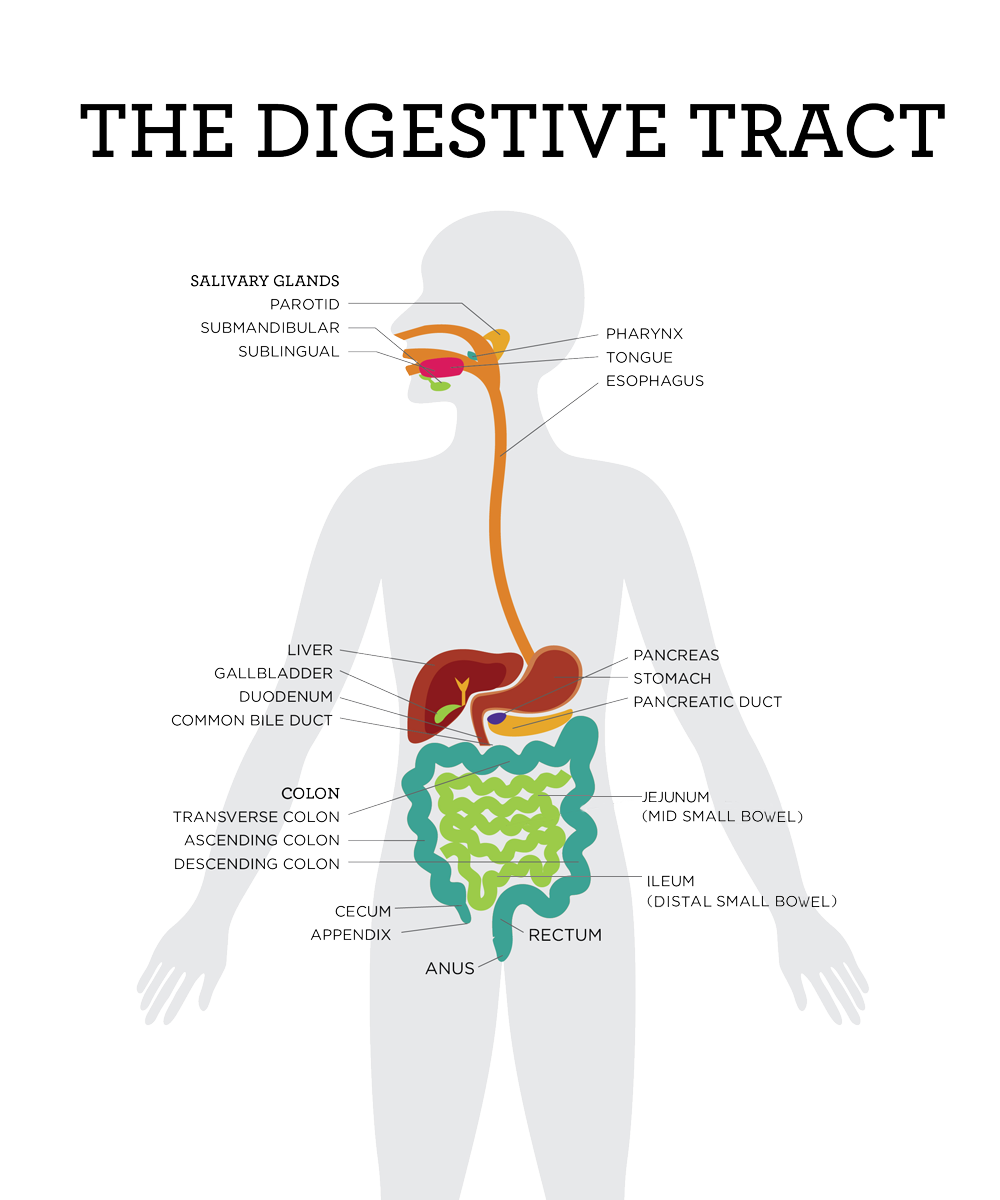



About Congenital Sucrase Isomaltase Deficiency Csid Cares
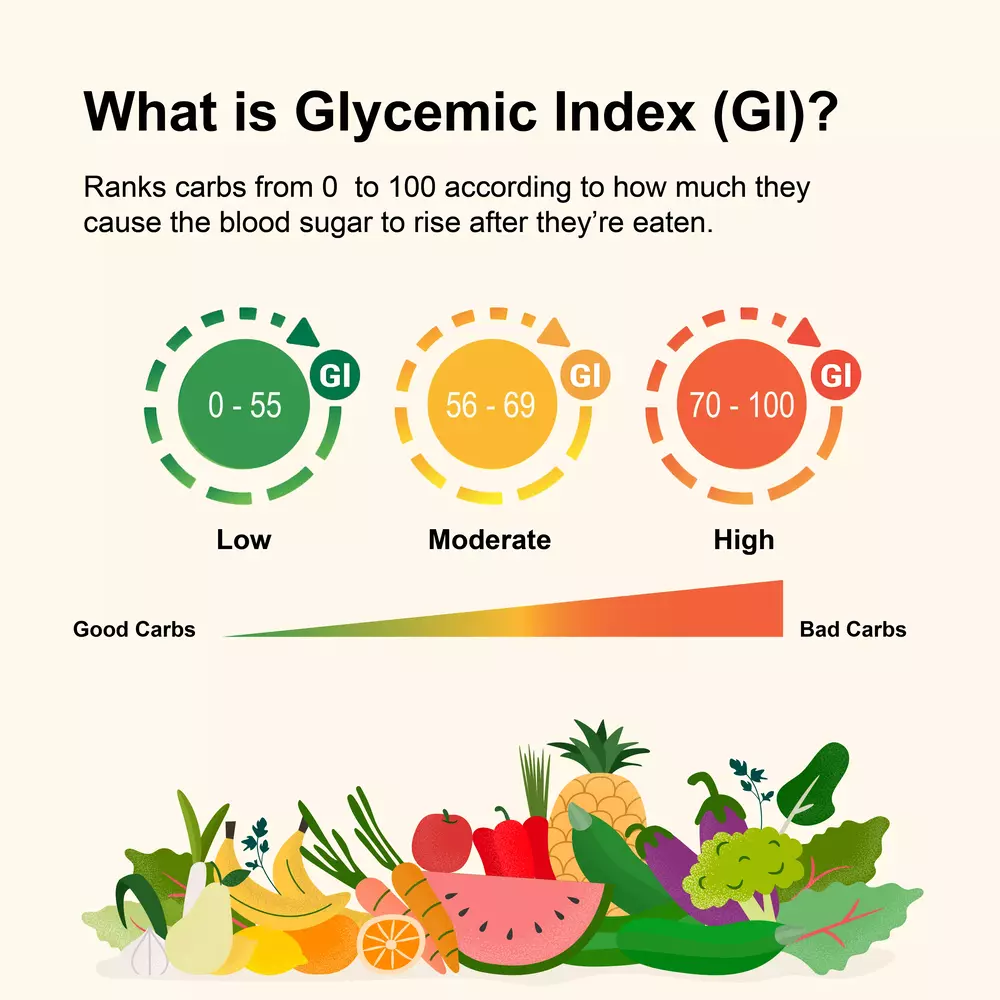



Discover The Good And Bad Of Carbohydrate
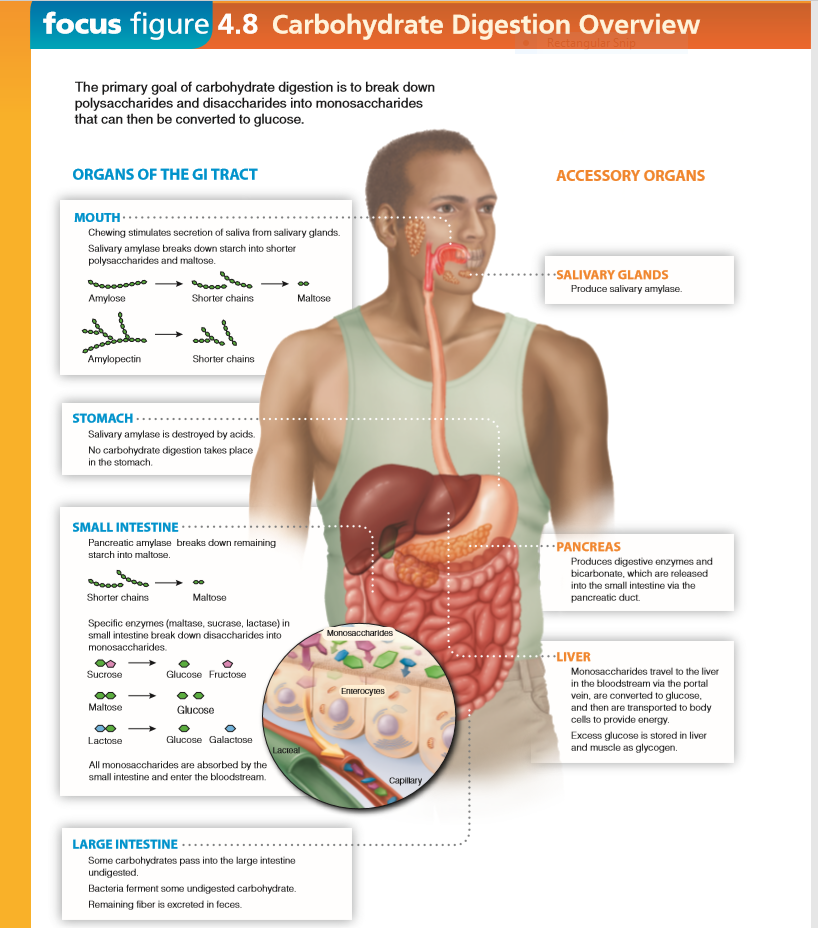



Solved Focus Figure 4 8 Carbohydrate Digestion Overview 4 Chegg Com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/blood-sugar-levels-after-eating-5118330-DD-V2-4f6a68ee274d4469820c4ad9d71cbd52.jpg)



What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating




Glucose Absorption An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Comprehensive Health 2nd Edition Page 70 86 Of 4




Chemical Digestion And Absorption A Closer Look Anatomy And Physiology Ii




Solved Focus Figure 4 8 Carbohydrate Digestion Overview 4 Chegg Com



1




Carbohydrate Digestion Absorption Enzymes Process And More




Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
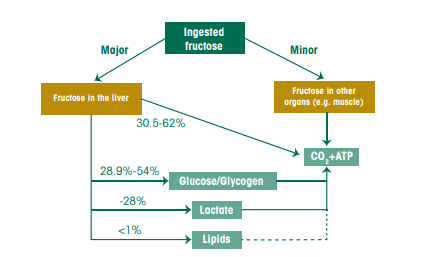



Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption The Canadian Sugar Institute
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/simple-and-complex-carbohydrates-and-diabetes-1087570-ADD-FINAL-V2-d27e373ab541449ba70bb26ff5f7cf71.png)



What To Know About Simple Vs Complex Carbohydrates



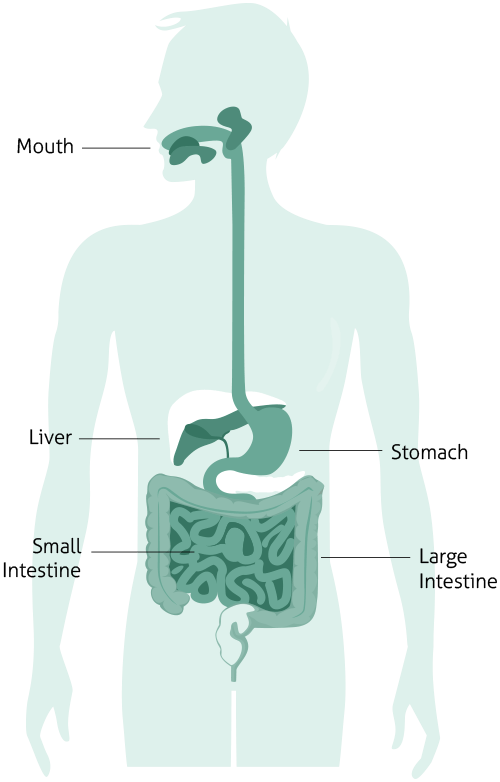
The Digestive System




Carbohydrates Crossword Wordmint




Digestion And Absorption Ck 12 Foundation
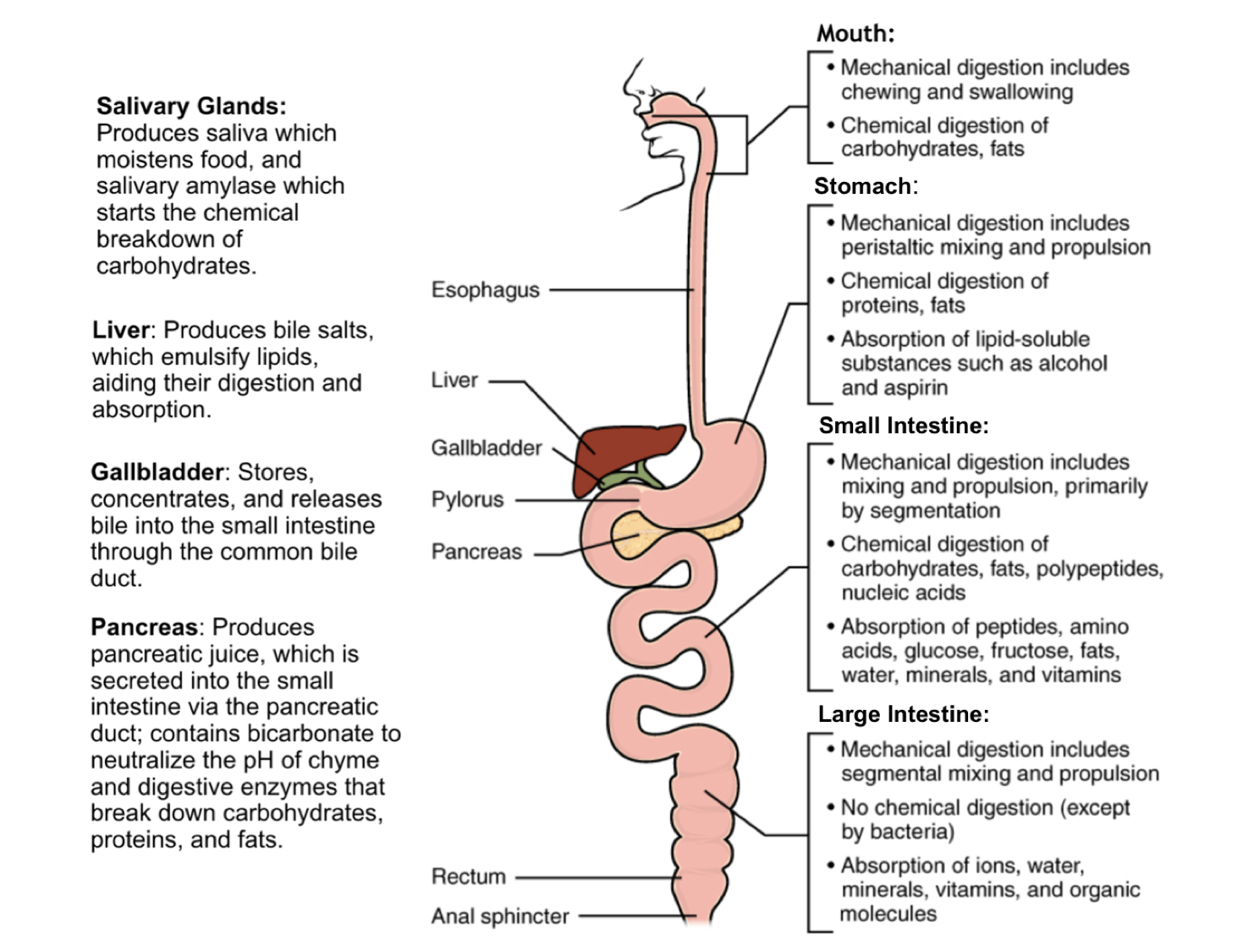



The Digestive System Nutrition Science And Everyday Application
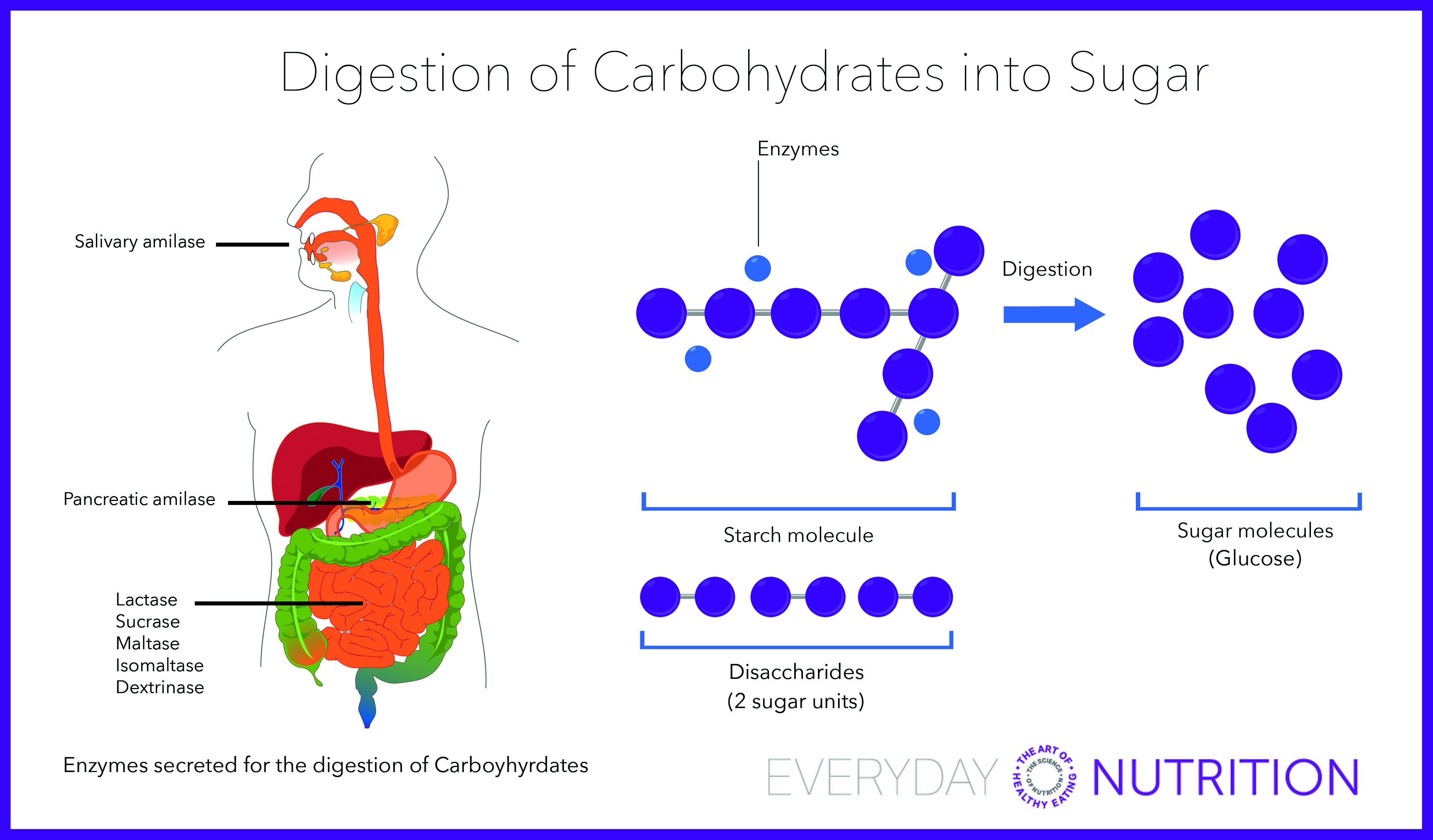



Everyday Nutrition The First Thing You Should Do For Your Health Better Energy And Weightloss




Blood Sugar After Eating What Happens Levels And More




Carbohydrates The Complete Guide To Understanding Carbs Ketogenic Com
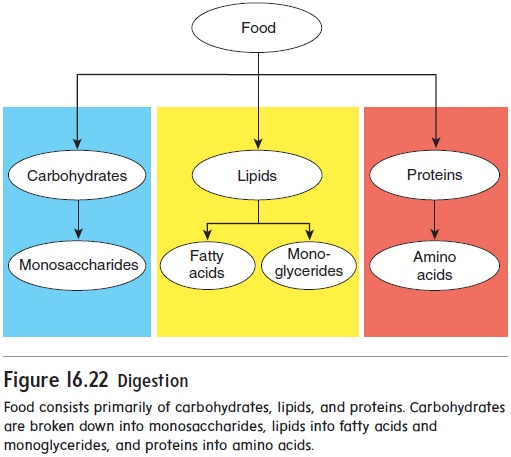



Digestion Absorption And Transport In Digestive System




Carbohydrates Sciencedirect



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates
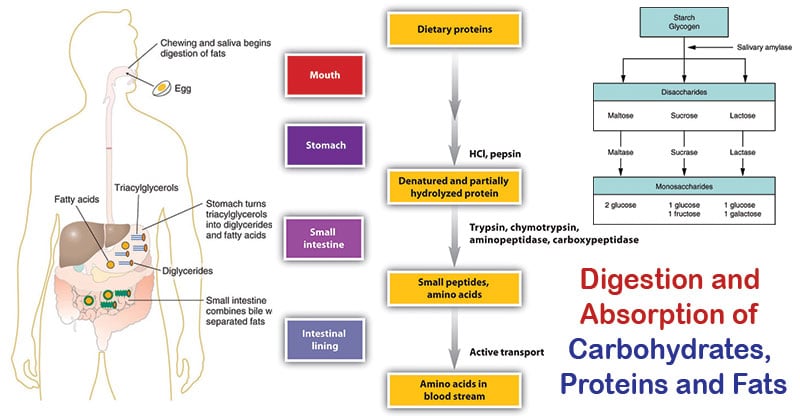



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Proteins And Fats




What Are The Key Functions Of Carbohydrates



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates




How The Human Body Break Down And Digest Food Britannica




Carbohydrates In The Diet Osu Fact Sheets Oklahoma State



Carbs Vs Sugar What S The Difference And Why It Matters




What Are Macronutrients Healthy Outcome For Teens



2




Torrente Sanguineo Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



1




Digestion And Absorption Ck 12 Foundation




Carbohydrates Sciencedirect
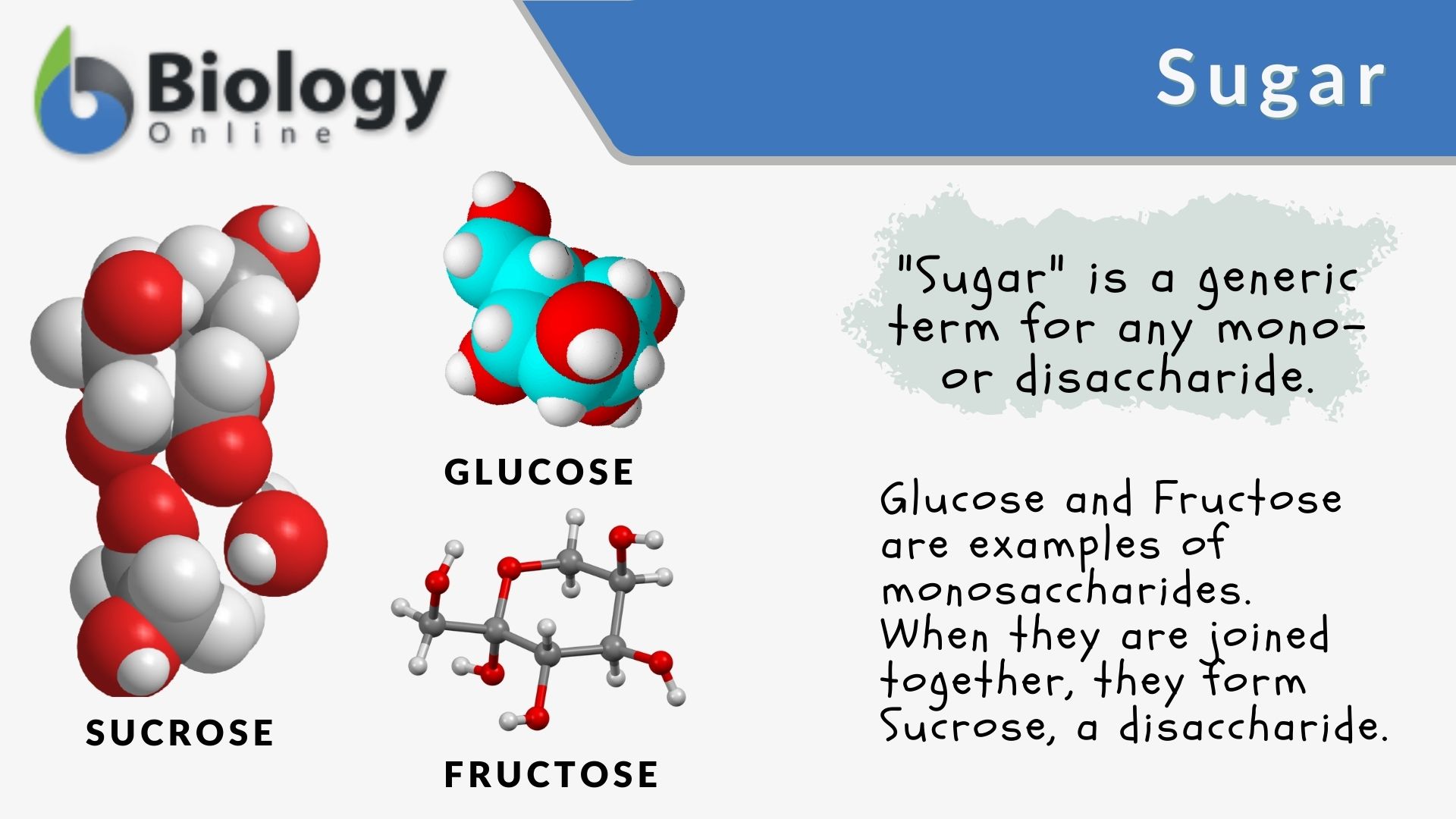



Sugar Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary



Differences Between Sugar And Starch Difference Between



Carbohydrates




What Are The Steps To Digestion For Carbohydrates
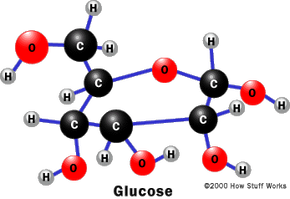



Carbohydrates How Food Works Howstuffworks




Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption Process End Products Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
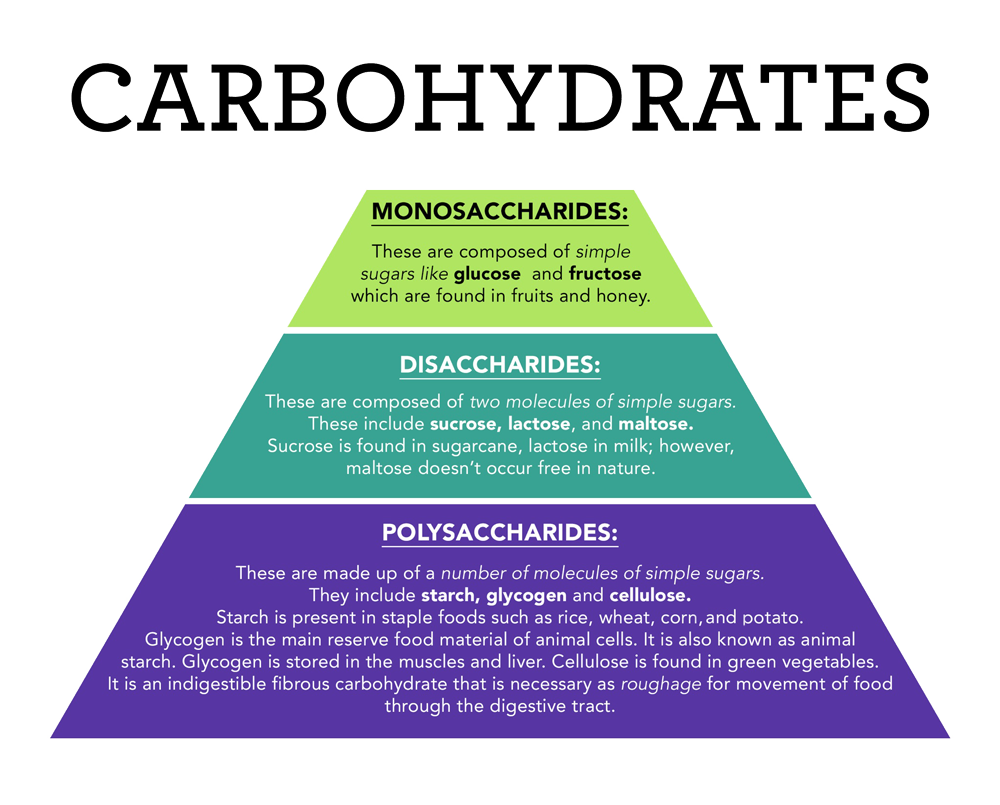



About Congenital Sucrase Isomaltase Deficiency Csid Cares



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates




Carbohydrates Sciencedirect




Chapter Chemical Digestion And Absorption Bio 140 Human Biology I Textbook Libguides At Hostos Community College Library




4 3 Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Medicine Libretexts




Learn About Carbohydrate Digestion Chegg Com




Carbohydrates And Dietary Fibre Lunn 07 Nutrition Bulletin Wiley Online Library
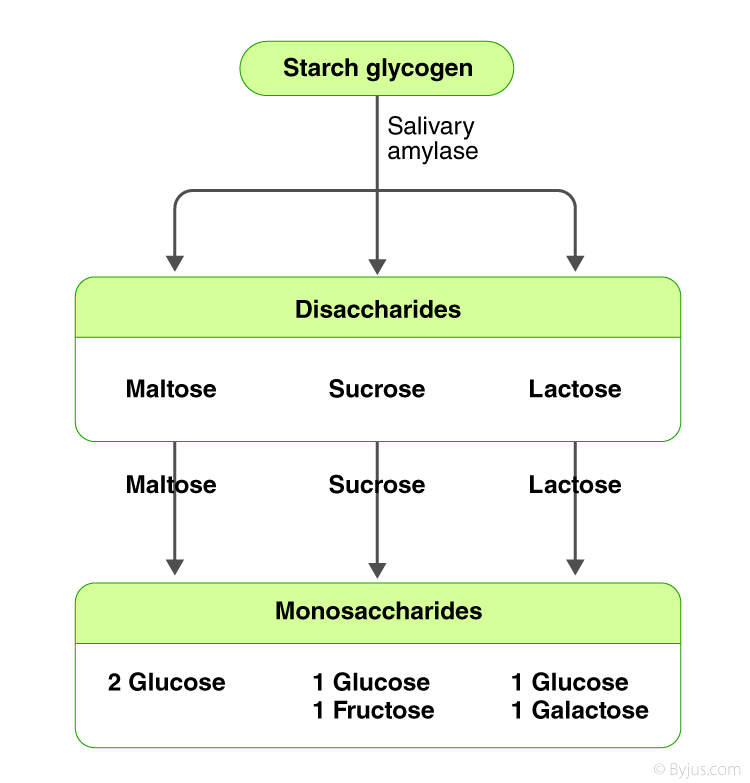



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Proteins And Lipids
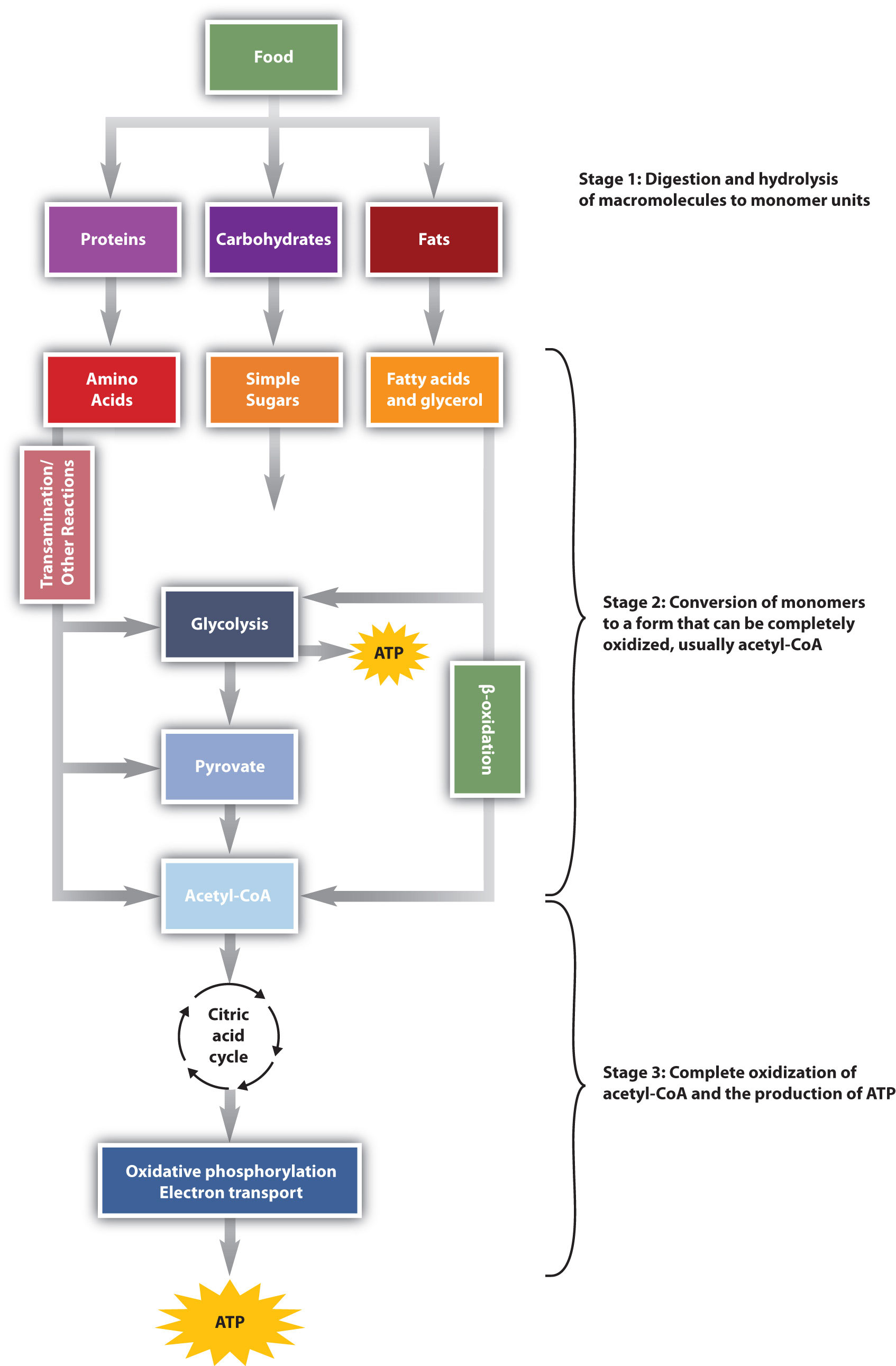



2 Stage I Of Catabolism Chemistry Libretexts



Digestion And Absorption Of Carbohydrates Human Nutrition Deprecated
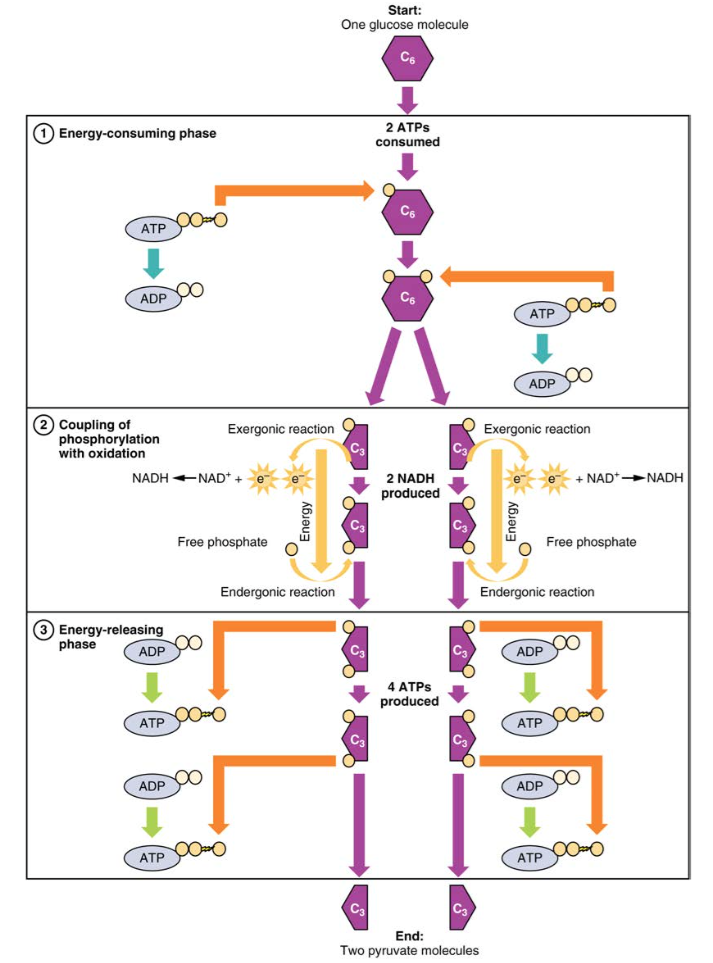



Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii




Glycemic Index Wikipedia
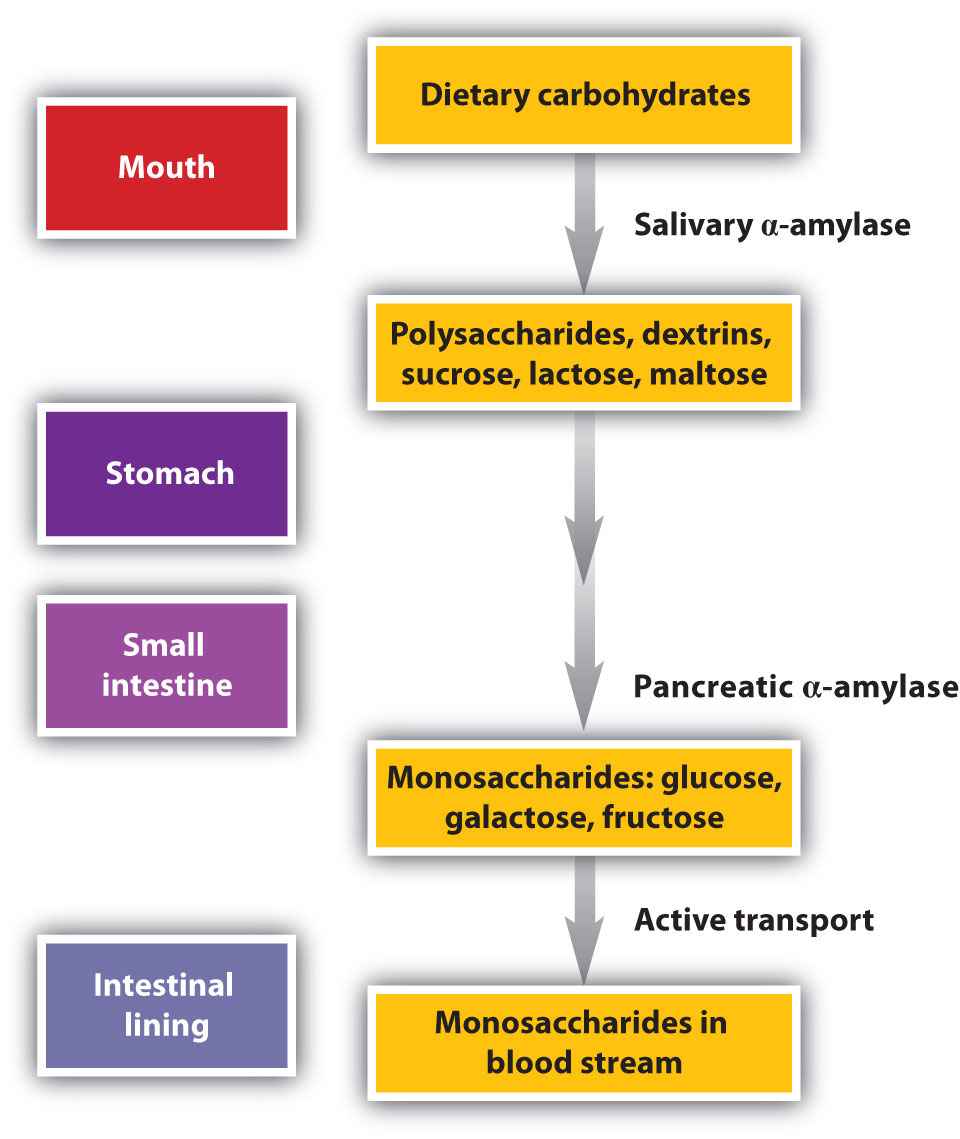



2 Stage I Of Catabolism Chemistry Libretexts



Carbohydrates



2
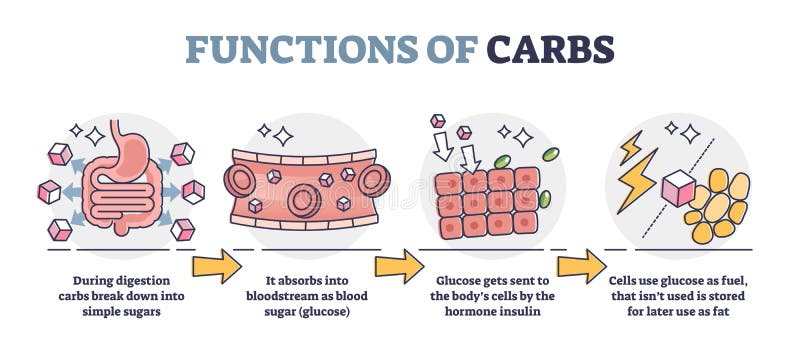



Functions Of Carbs And Carbohydrates In Digestive System Outline Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Protein Concept




Carbohydrate Metabolism Wikipedia
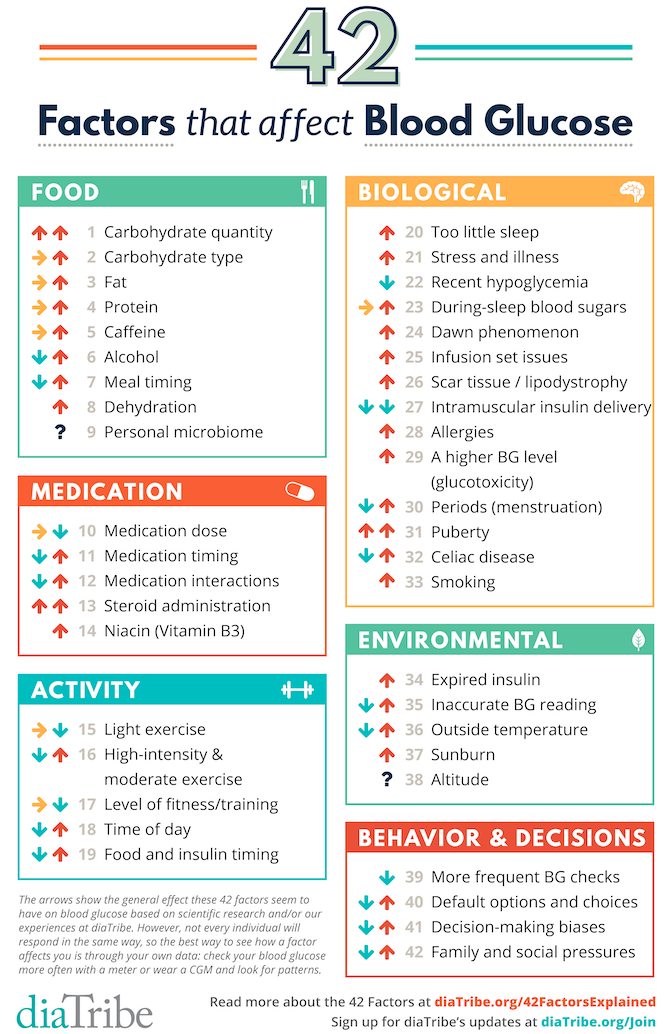



The Basics Of Nutrition And Diabetes Incontrol Nutrition




Carbohydrate Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Carbohydrates And Blood Sugar The Nutrition Source Harvard T H Chan School Of Public Health
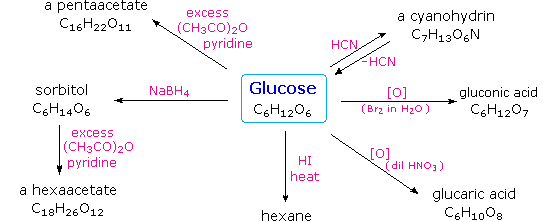



Carbohydrates




Solved Best Completes The Vie 1019 1 Carbohydrate Digestion Chegg Com



1



1
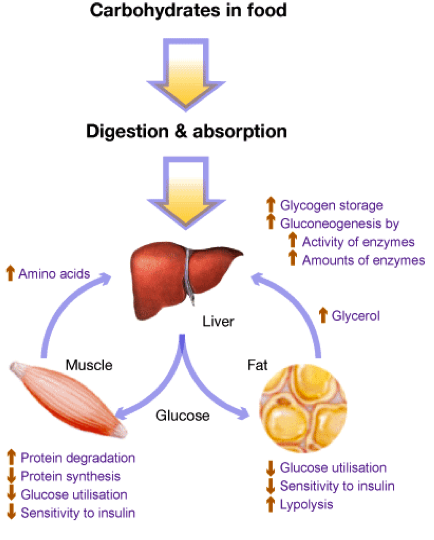



The War On Carbohydrates Tidal Elite Performance Center



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿